This month we have another feature from Dr. Page Crow, DC, owner and operater of Crow Chiropractic & Acupuncture. Page is not only an amazing chiropractor, but is also well versed in holistic approaches to healing the entire human body.
There are many health disorders of the human body. Underlying most of these
health challenges is the condition of inflammation. The inflammatory reaction by
the body is a healthy response, giving-rise to tissue repair body healing. Yet
inflammation can become a harmful condition if allowed to persist in the body and
become chronic. Many health problems can be made better if inflammation is
recognized and treated.
Inflammation is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful
stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, irritants, and is a protective response
involving immune cells, blood vessels and molecular mediators. The function of
inflammation is to eliminate the initial cause of cell injury, clear-out injured or
dead cells and activate tissue repair. The five classical signs of inflammation are
heat, pain, redness, swelling and loss of function. Inflammation is a generic
response. It is considered a mechanism of innate (automatic) immunity, as
compared to adaptive immunity, which is specific for each pathogen. Too little
inflammation could lead to progressive tissue destruction by the harmful stimulus
and compromise the survival of the organism. In contrast, chronic inflammation is
associated with many various diseases, such as hay fever, periodontal disease,
atherosclerosis and osteoarthritis.
Inflammation can be classified as either acute or chronic. At the cellular level,
acute inflammation is the initial response by the body to harmful stimuli and is
achieved by the increased movement of plasma (body fluids) and leukocytes (white
blood cells) from the blood vessels into the injured tissues. A series of biochemical
events propagates and progresses the inflammatory response, involving the local
vascular system, the immune system and various cells within the injured tissue.
At the whole-body level, inflammation may also be associated with flu-like
symptoms, including fever, chills, fatigue, headache, loss of appetite and muscle
stiffness. Prolonged inflammation, known as chronic inflammation, leads to a
progressive shift in the type of cells present at the site of inflammation and is
characterized by simultaneous destruction and healing with fibrosis in body tissue
from the inflammatory process.
Inflammation can affect many organs & structures in the human body. When these
various tissues are affected by inflammation, medical science has distinct
diagnostic names for each variation of inflammatory disease. Inflammation in the
body has even been shown to affect the brain\mind, causing specific forms of
depression. The body affects the mind, an example of a psychoneuroimmunity
reaction (mind\nervous\immune). A 5-year research study involving over 14,000
patients with depression noted that patients with depression had upwards of 46%
more C-reactive protein in their blood, a marker for inflammation. Efforts to
reduce inflammation in the body reduced the incidence of depression.
INFLAMMATION & AGE
A common inflammatory process of babies & children is otitis externa & otitis
media. These are forms of both acute & chronic inflammation. Inflammation
swells the internal\external tissues of the ear & the eustachain tubes that drain the
inner-ear. Blockage & swelling get worse. The body’s internal ear fluids
accumulate. If the normal drainage for the ear does not function, the body will
burst the tympanic membrane (ear drum), releasing blood & pus onto the pillow.
A more common chronic inflammatory degenerative process of adults includes the
small & large intestine. Many names are given to gut problems, including irritable
bowel disease, colitis, constipation, inflammatory bowel disease, crohn’s disease,
ulcerative colitis and others. The common symptoms include indigestion,
imbalance in bowel habits (too few\too many), bloody stools, painful gut, inability
to eat certain foods, bleeding from the bum and more.
 Auto-immune means the body attacks itself. Many organs and tissues can be
affected by personal attack: skin, muscles, bones, the nervous system, blood, the
gut, thyroid and the brain. Moreover, all tissues, organs and structures can be
adversely affected by the body’s immune system attacking its own body.
Auto-inflammatory diseases refer to problems within the immune system, which
usually fights off viruses, bacteria and infection. The problem causes your immune
cells to attack your own body by mistake. This can cause swelling that produces
fever, rash, joint swelling or serious buildup of a blood protein in your organs.
Possible triggers for autoimmune reactions include pre-existing adverse health.
ex’s: diabetes and obesity, fatigue, stress, food intake, hormone imbalance,
pesticides, toxins exposure & ingestion, heavy metals poisoning. External adverse
environmental influences can cause body damage. Unhealthy psyche levels,
including worry, fear & anger, contribute to immune weakness and autoimmune
reactivity.
Auto-immune means the body attacks itself. Many organs and tissues can be
affected by personal attack: skin, muscles, bones, the nervous system, blood, the
gut, thyroid and the brain. Moreover, all tissues, organs and structures can be
adversely affected by the body’s immune system attacking its own body.
Auto-inflammatory diseases refer to problems within the immune system, which
usually fights off viruses, bacteria and infection. The problem causes your immune
cells to attack your own body by mistake. This can cause swelling that produces
fever, rash, joint swelling or serious buildup of a blood protein in your organs.
Possible triggers for autoimmune reactions include pre-existing adverse health.
ex’s: diabetes and obesity, fatigue, stress, food intake, hormone imbalance,
pesticides, toxins exposure & ingestion, heavy metals poisoning. External adverse
environmental influences can cause body damage. Unhealthy psyche levels,
including worry, fear & anger, contribute to immune weakness and autoimmune
reactivity.
Autoimmune diseases outnumber heart disease & cancer in the U.S. Chronic
inflammation is the main consequence of an autoimmune reaction and occurs when
the anti-inflammatory system of the body is impaired. It becomes important to
reduce the number of things triggering the body into the inflammatory response. It
is equally important to practice the many safe\best practices that reduce, eliminate
and prevent inflammation. These practices should be made routine throughout a
person’s life, not just in time of dis-health.
Western medical practices use pharmaceutical drugs to combat inflammation.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs include aspirin, ibuprofen & naproxen.
Steroid-type drugs include prednisone and many steroid-type variations. The
anti-malaria drug, hydroxychloroquine is in the news and a common option for
medics to use when reducing inflammation.
If water is the #1 anti-inflammatory compound, then chronic dehydration may be
one the more common underlying causes for inflammation. Second in
effectiveness, juicing fresh greenfoods (algae, alfalfa, dulce, seaweed, kale, celery)
yields potent anti-inflammatory nutrition.
Foods that are reported to reduce inflammation include colorful fruits, broccoli,
healthy fats, green tea, turmeric, bell peppers, pineapple, leafy green vegetables
and dark chocolate.
It has been said, “Stop doing what makes you sick. Start doing things that make
you healthy.” The more healthy things you do, the better you get.
In humans on a Western diet, the omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid
arachidonic acid (ARA) makes a significant contribution to the fatty acids
present in the membrane phospholipids of cells involved in inflammation.
We are what we eat. Fried foods contain large amounts of omega-6
polyunsaturated fatty acids. When a person reduces intake of fried foods,
chronic inflammation reduces in the body.
Cannabis is emerging from decades of illegality in our world. Research is ongoing
involving the use of cannabis for anti-inflammation use. Cannabis contains over
450 different substances, only three of which are responsible for its intoxicating
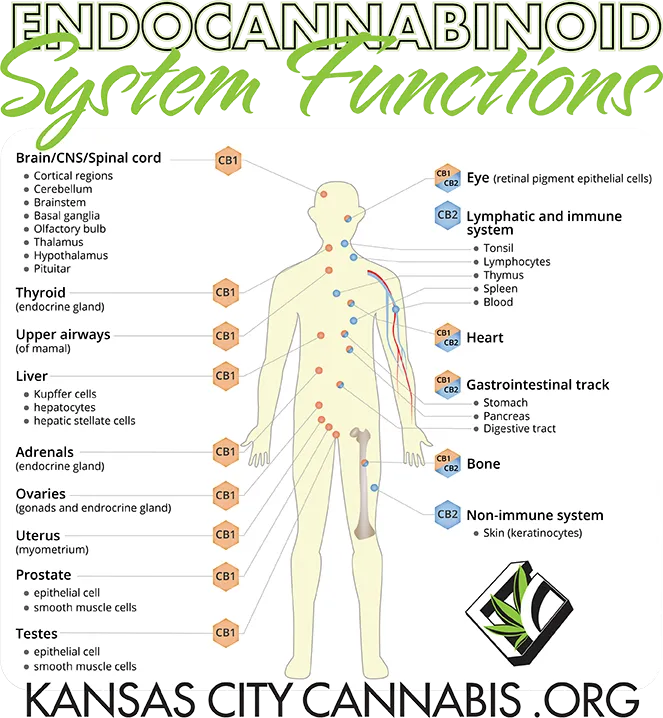
effect. Cannabis activates the endocannabinoid systems, specifically two receptors
in the body, CB1 and CB2. While the CB1 receptor in the central nervous system
influences perception, the CB2 receptor in all tissues plays a crucial role in
inhibiting inflammation. If the receptor is activated, the cell releases fewer
pro-inflammatory signal substances, or cytokines. Scientists have now discovered
that the substance, beta-carophyllene, which composes between 12 and 35 percent
of the cannabis plant’s essential oil, activates the CB2 receptor selectively.
note: This blog on inflammation is meant for information purpose only. It is not
meant to diagnose or treat disease. If you are experiencing symptoms of
inflammation, you should communicate this with your healthcare provider.

 Afternoon: Within walking distance of your breakfast is the City Market Farmers Market. Arriving early allows you to beat the crowds and browse the various stalls at your leisure. Here, you'll find everything from locally grown fresh produce to artisanal cheese, handmade crafts, and more. It's the perfect place to grab a cup of coffee, enjoy breakfast from one of the food vendors, and soak in the vibrant atmosphere.
Afternoon: Within walking distance of your breakfast is the City Market Farmers Market. Arriving early allows you to beat the crowds and browse the various stalls at your leisure. Here, you'll find everything from locally grown fresh produce to artisanal cheese, handmade crafts, and more. It's the perfect place to grab a cup of coffee, enjoy breakfast from one of the food vendors, and soak in the vibrant atmosphere.
 Evening: Your Saturday night in Kansas City wouldn't be complete without experiencing its renowned BBQ culture. Head to Q39, a top-tier, full-service barbecue restaurant where you can savor expertly smoked meats and innovative dishes like the BBQ Pork Belly and Apple Coleslaw. Don't forget to try their signature cocktails for the complete culinary experience.
Evening: Your Saturday night in Kansas City wouldn't be complete without experiencing its renowned BBQ culture. Head to Q39, a top-tier, full-service barbecue restaurant where you can savor expertly smoked meats and innovative dishes like the BBQ Pork Belly and Apple Coleslaw. Don't forget to try their signature cocktails for the complete culinary experience.
 Afternoon: After the museum, venture over to the Westport neighborhood. This part of town is known for its hip, relaxed vibe, boasting a variety of boutiques, coffee shops, and restaurants. Have lunch at Westport Café and Bar, a charming bistro offering French-inspired dishes and a fine selection of wines.
Afternoon: After the museum, venture over to the Westport neighborhood. This part of town is known for its hip, relaxed vibe, boasting a variety of boutiques, coffee shops, and restaurants. Have lunch at Westport Café and Bar, a charming bistro offering French-inspired dishes and a fine selection of wines.













 Auto-immune means the body attacks itself. Many organs and tissues can be
affected by personal attack: skin, muscles, bones, the nervous system, blood, the
gut, thyroid and the brain. Moreover, all tissues, organs and structures can be
adversely affected by the body’s immune system attacking its own body.
Auto-inflammatory diseases refer to problems within the immune system, which
usually fights off viruses, bacteria and infection. The problem causes your immune
cells to attack your own body by mistake. This can cause swelling that produces
fever, rash, joint swelling or serious buildup of a blood protein in your organs.
Possible triggers for autoimmune reactions include pre-existing adverse health.
ex’s: diabetes and obesity, fatigue, stress, food intake, hormone imbalance,
pesticides, toxins exposure & ingestion, heavy metals poisoning. External adverse
environmental influences can cause body damage. Unhealthy psyche levels,
including worry, fear & anger, contribute to immune weakness and autoimmune
reactivity.
Auto-immune means the body attacks itself. Many organs and tissues can be
affected by personal attack: skin, muscles, bones, the nervous system, blood, the
gut, thyroid and the brain. Moreover, all tissues, organs and structures can be
adversely affected by the body’s immune system attacking its own body.
Auto-inflammatory diseases refer to problems within the immune system, which
usually fights off viruses, bacteria and infection. The problem causes your immune
cells to attack your own body by mistake. This can cause swelling that produces
fever, rash, joint swelling or serious buildup of a blood protein in your organs.
Possible triggers for autoimmune reactions include pre-existing adverse health.
ex’s: diabetes and obesity, fatigue, stress, food intake, hormone imbalance,
pesticides, toxins exposure & ingestion, heavy metals poisoning. External adverse
environmental influences can cause body damage. Unhealthy psyche levels,
including worry, fear & anger, contribute to immune weakness and autoimmune
reactivity.

















